
FSH and LH then stimulate the testis to produce testosterone. When testosterone levels are low, gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is released by the hypothalamus, which in turn stimulates the pituitary gland to release FSH and LH.
Hormone (FSH) and gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Hormones involved are luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating Pituitary, and testicular endocrine glands. Testosterone regulation by cooperation between the hypothalamus, The heart beats faster than normal, pushing blood to the muscles, heart, and other vital organs. As epinephrine circulates through the body, it brings on a number of physiological changes.

Testosterone, like all hormones, works via long distance signaling and is regulated by other hormones as illustrated below: These glands respond by pumping the hormone epinephrine (also known as adrenaline) into the bloodstream. In adult males, testosterone plays a key role in the development of reproductive organs and it promotes the secondary sexual characteristics of body and facial hair, increased muscle and bone mass, and a deep voice.

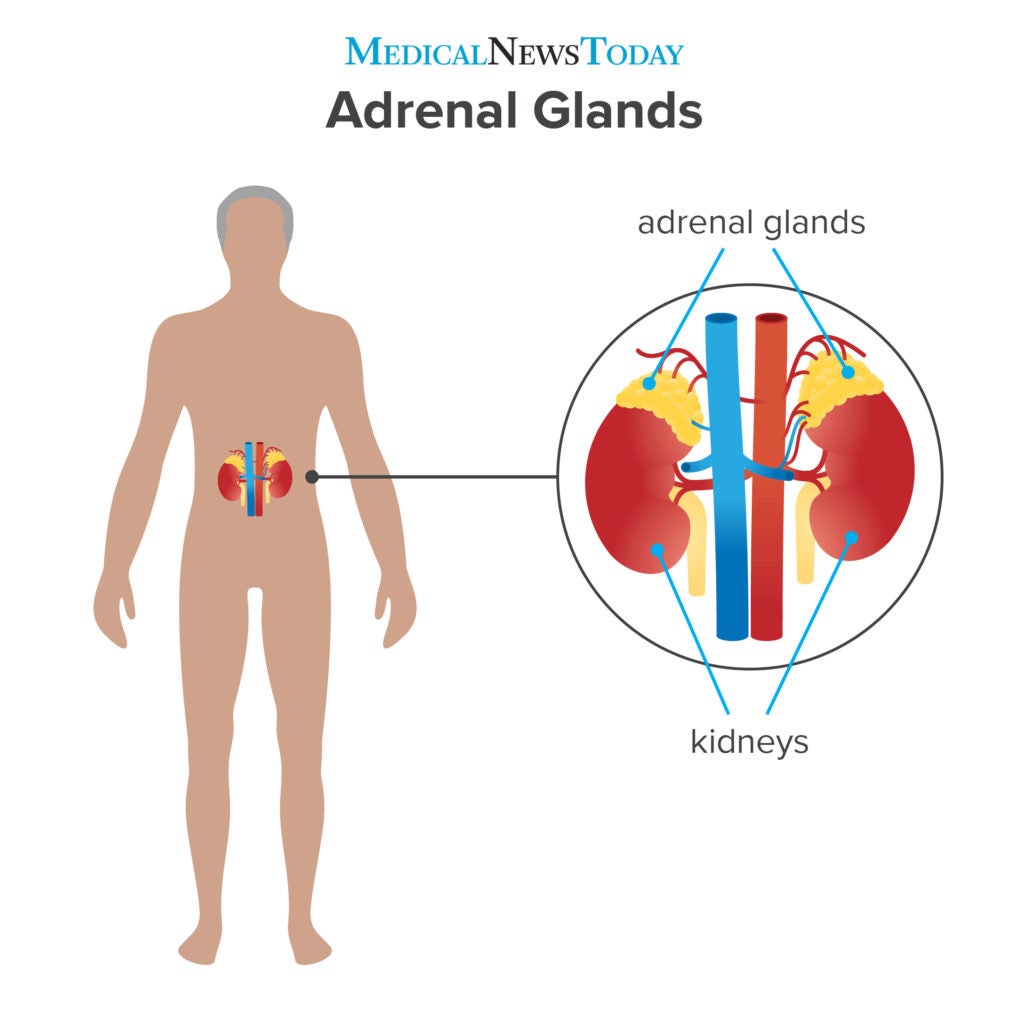
Identify the major mineralocorticoids, their biologic actions, and their target organs or tissues. The adrenal glands produce glucocorticoids and androgens, which are sex hormones that promote masculinity.Understand the cellular mechanism of action of adrenal cortical hormones and identify their major physiologic actions, particularly during injury and stress.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
